Hair is not just an essential part of our appearance but also a reflection of our overall health. Hair diseases can significantly impact self-esteem and quality of life. Understanding these conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for maintaining healthy hair. This article explores common hair diseases, offering insights into their management and prevention.
Common Hair Diseases
- Alopecia Areata
- Description: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss in patches.
- Symptoms: Sudden hair loss in round or oval patches, usually on the scalp but can affect other body parts.
- Causes: Genetic predisposition, stress, and other autoimmune conditions.
- Treatment: Corticosteroid injections, topical immunotherapy, and oral immunosuppressants.
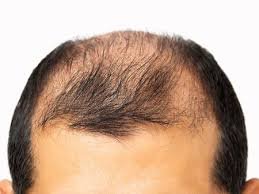
- Androgenetic Alopecia
- Description: Also known as male or female pattern baldness, this is the most common type of hair loss.
- Symptoms: Gradual thinning of hair on the scalp, typically starting at the hairline and crown in men, and broadening part lines in women.
- Causes: Genetic factors and hormonal changes, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
- Treatment: Minoxidil, finasteride (for men), and hair transplantation.
- Telogen Effluvium
- Description: A temporary condition where hair falls out after a stressful event, illness, or hormonal changes.
- Symptoms: Diffuse thinning of hair across the scalp.
- Causes: Physical or emotional stress, surgery, severe illness, childbirth, or rapid weight loss.
- Treatment: Addressing the underlying cause, nutritional support, and sometimes minoxidil.
- Tinea Capitis
- Description: A fungal infection of the scalp, also known as scalp ringworm.
- Symptoms: Scaly patches of hair loss, itching, and sometimes painful lesions.
- Causes: Fungal organisms such as Trichophyton and Microsporum species.
- Treatment: Oral antifungal medications like griseofulvin or terbinafine, and antifungal shampoos.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Description: A common inflammatory skin condition affecting the scalp, causing flaky scales and itchy, red skin.
- Symptoms: Dandruff, greasy patches of skin covered with flaky white or yellow scales.
- Causes: Yeast (Malassezia), oily skin, stress, and genetic factors.
- Treatment: Medicated shampoos containing ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione, and topical corticosteroids.
- Psoriasis
- Description: A chronic autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to multiply rapidly, leading to scaling on the skin’s surface.
- Symptoms: Red patches covered with thick, silvery scales, often affecting the scalp.
- Causes: Genetic factors, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers.
- Treatment: Topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic medications.
- Trichotillomania
- Description: A psychological disorder characterized by the compulsive urge to pull out one’s hair.
- Symptoms: Noticeable hair loss, bald patches, and sometimes skin infections.
- Causes: Stress, anxiety, or other underlying psychological issues.
- Treatment: Behavioral therapy, counseling, and sometimes medications.
- Lichen Planopilaris
- Description: A rare inflammatory condition that affects the scalp and hair follicles, leading to scarring and permanent hair loss.
- Symptoms: Red or purple patches, scalp tenderness, and hair loss.
- Causes: Autoimmune response.
- Treatment: Corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agents, and antimalarial drugs.
Managing Hair Diseases
Managing hair diseases involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and hair care practices. Here are some general tips for maintaining hair health and managing common hair diseases:
- Consult a Dermatologist: Seek professional advice for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
- Healthy Diet: Ensure a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals essential for hair health, such as iron, zinc, vitamin D, and biotin.
- Gentle Hair Care: Use mild shampoos and conditioners, avoid excessive heat styling, and handle hair gently to prevent breakage.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, and regular exercise.
- Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Hairstyles that pull on the hair can cause traction alopecia. Opt for loose styles to reduce stress on hair follicles.
- Regular Scalp Care: Keep the scalp clean and free from infections. Use medicated shampoos if prone to conditions like dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis.
Conclusion
Hair diseases can significantly impact an individual’s appearance and self-esteem, but understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatments can help manage these conditions effectively. By seeking professional advice, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and practicing good hair care habits, individuals can improve their hair health and reduce the impact of hair diseases. Continued research and advancements in dermatology will further enhance our ability to treat and prevent these conditions, ensuring healthier hair for all.